Have you ever pondered whether that morning cup of coffee is doing more than just waking you up? Coffee, one of the most consumed beverages worldwide, often stirs debates concerning its impact on health and wellness. This discussion revolves largely around its influence on metabolism. Does drinking coffee positively affect metabolism? In this comprehensive guide, we will explore this topic in depth, providing you with a detailed understanding of how coffee interacts with metabolic processes.
Buy Coffee For Better Metabolism
Understanding Metabolism
Metabolism is a vital process involving a series of chemical reactions within the body that converts food into energy. It is essential for the maintenance of basic life functions, such as breathing, blood circulation, and cell repair. The rate at which your body burns calories to perform these functions is known as your metabolic rate. It can be influenced by several factors, including age, gender, muscle mass, and even dietary choices.
Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)
Your Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) is the number of calories your body needs at rest to maintain life-sustaining functions. It accounts for approximately 60-75% of your daily calorie expenditure. Factors affecting BMR include age, weight, height, gender, and genetic predisposition.
Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE)
Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE) is the total amount of calories you burn in a day, accounting for BMR, physical activity, and the thermic effect of food (TEF). Understanding your TDEE can help comprehend how various factors like diet and exercise impact weight management and overall metabolic health.
Coffee and Its Primary Components
Before delving into coffee’s impact on metabolism, it is imperative to understand the primary components of coffee. These include caffeine, antioxidants, and diterpenes. Each plays a unique role in influencing bodily functions, including metabolic processes.
Caffeine
Caffeine is the most widely researched component of coffee, recognized for its stimulating effects on the central nervous system. It works by blocking the inhibitory neurotransmitter adenosine, leading to increased neuronal firing and the release of other neurotransmitters like dopamine and norepinephrine. This action results in enhanced alertness and reduced fatigue.
Antioxidants
Coffee is a rich source of antioxidants, such as chlorogenic acids, which help combat oxidative stress by neutralizing free radicals in the body. Antioxidants play a role in preventing cellular damage, which can have various benefits for metabolic health and beyond.
Diterpenes
Diterpenes, such as cafestol and kahweol found in coffee, have been linked to both positive and negative health effects. These components are known to exert antioxidant properties but may also affect cholesterol levels, especially when coffee is brewed unfiltered.

Explore Metabolism-Boosting Coffee Options
The Role of Coffee in Boosting Metabolism
The primary discussion around coffee and metabolism typically revolves around caffeine’s role in boosting metabolic rate. Let’s delve into how coffee might influence your metabolic processes.
Caffeine and Thermogenesis
Thermogenesis refers to the process of heat production in the body, during which calories are burned. Caffeine is known to enhance thermogenesis, thereby temporarily increasing your metabolic rate and aiding in calorie burning. This effect can be particularly beneficial for those looking to lose weight or maintain weight loss.
Fat Oxidation
Several studies suggest that caffeine can increase the rate of fat oxidation, meaning your body may become more efficient at using fat as a fuel source. This effect can be especially pronounced during exercise, where caffeine intake before physical activity has shown to enhance performance and fat burning.
Appetite Suppression
While caffeine’s impact on appetite is still an area of active research, some evidence suggests that it may temporarily reduce hunger and delay the onset of hunger pangs. This effect could contribute to a reduction in caloric intake, thereby indirectly affecting metabolic rate.
Coffee and Weight Management
Given coffee’s potential effects on metabolism, it’s worth assessing its influence on weight management. Though not a miracle solution, coffee can be a complementary element in a weight management regimen.
Enhancing Physical Performance
As mentioned earlier, caffeine can enhance physical performance by mobilizing fatty acids from the fat tissues and increasing levels of adrenaline. This increased alertness and endurance can lead to more effective workouts, burning more calories and aiding in weight management.
Long-term Weight Loss
While caffeine may boost metabolism and fat burning, its impact on long-term weight loss is less clear. Habitual coffee consumption over long periods might lead to tolerance, diminishing its stimulatory effects. Thus, coffee should be considered a tool, rather than the sole solution, in weight management strategies.
Coffee as a Part of a Balanced Diet
Incorporating coffee into a well-balanced diet rich in nutrients, while maintaining an active lifestyle, is crucial to maximizing its potential metabolic benefits. Relying solely on coffee without considering dietary habits and physical activity can undermine weight management efforts.

Potential Limitations and Caution
While coffee offers several potential metabolic benefits, there are precautions and limitations to its consumption. Overconsumption or dependence on caffeine can lead to unwanted side effects.
Possible Side Effects
Excessive caffeine intake can lead to side effects, including insomnia, nervousness, restlessness, stomach irritation, nausea, and increased heart rate. People who are sensitive to caffeine or those consuming large amounts should be cautious.
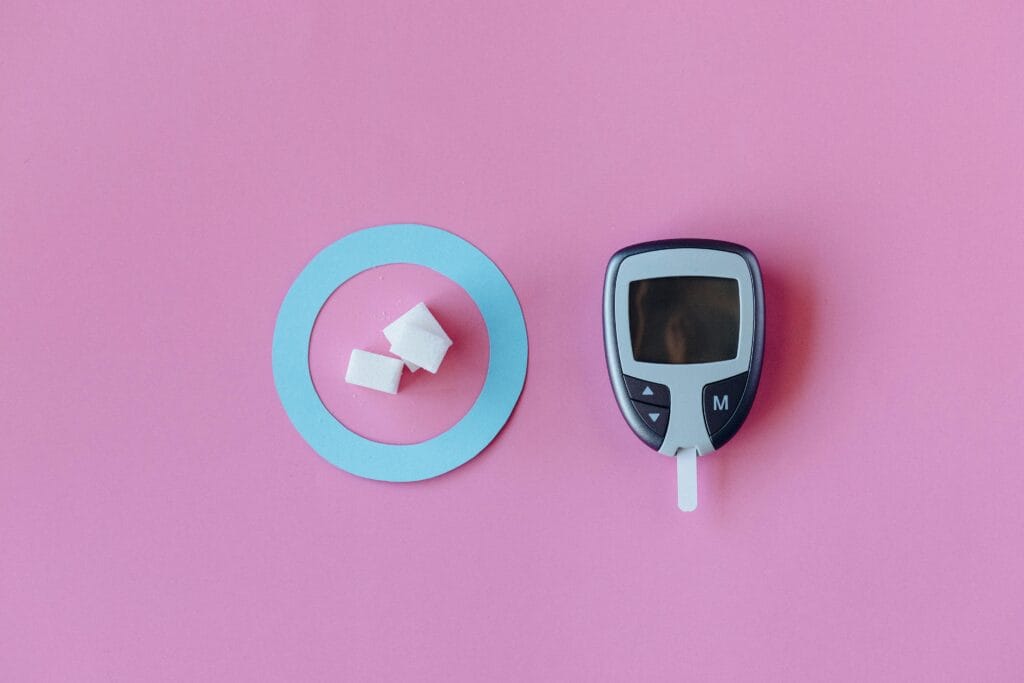
Impact on Blood Sugar
Some research has shown that caffeine may have short-term effects on insulin sensitivity, potentially affecting blood sugar levels. It is advisable for individuals with diabetes or blood sugar management challenges to monitor their coffee intake and consult healthcare professionals.
Balance and Moderation
Like any dietary component, coffee consumption is best approached with balance and moderation. It is important to tailor coffee intake to individual tolerance levels and health conditions, avoiding excessive consumption that could negate its potential benefits.
Conclusion
After exploring the multifaceted relationship between coffee and metabolism, you might appreciate the role your morning brew plays in your overall metabolic health. While coffee holds potential benefits, primarily due to its caffeine content, it should be enjoyed in moderation and as part of a balanced lifestyle to achieve optimal results. Remember, coffee is just one piece of the puzzle, and a holistic approach to wellness, involving a nutritious diet and regular physical activity, will yield the best outcomes for metabolic health.



